Aircraft Sealant Application Guide
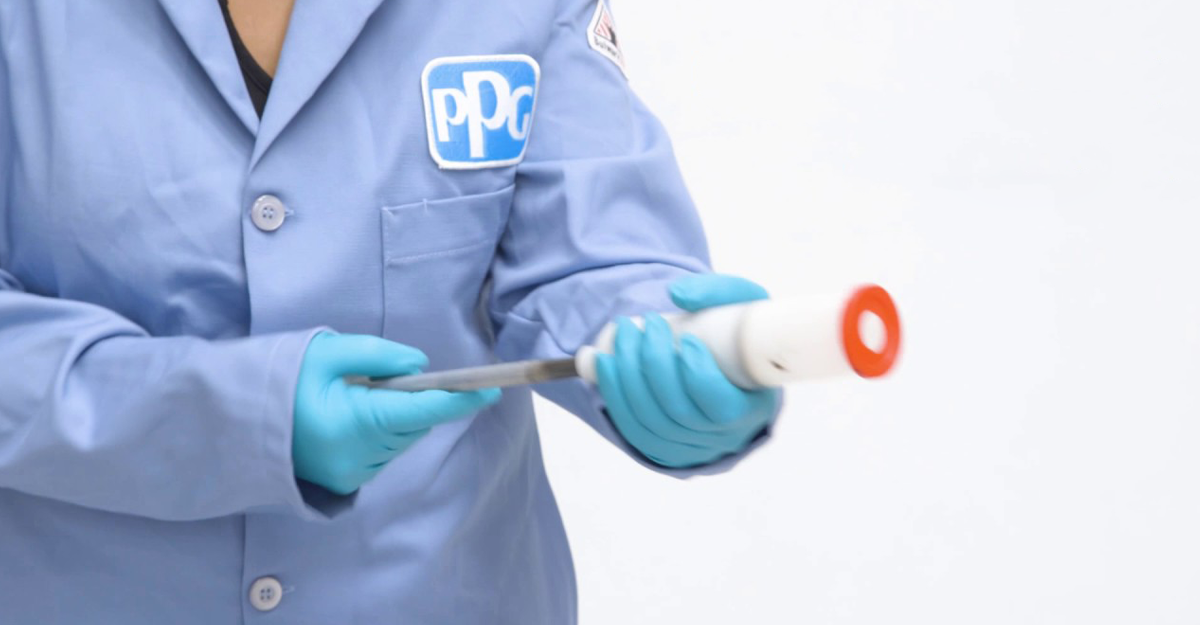
While selecting the right sealant is the first step, additional decisions need to be made that will affect the application of the sealant itself.
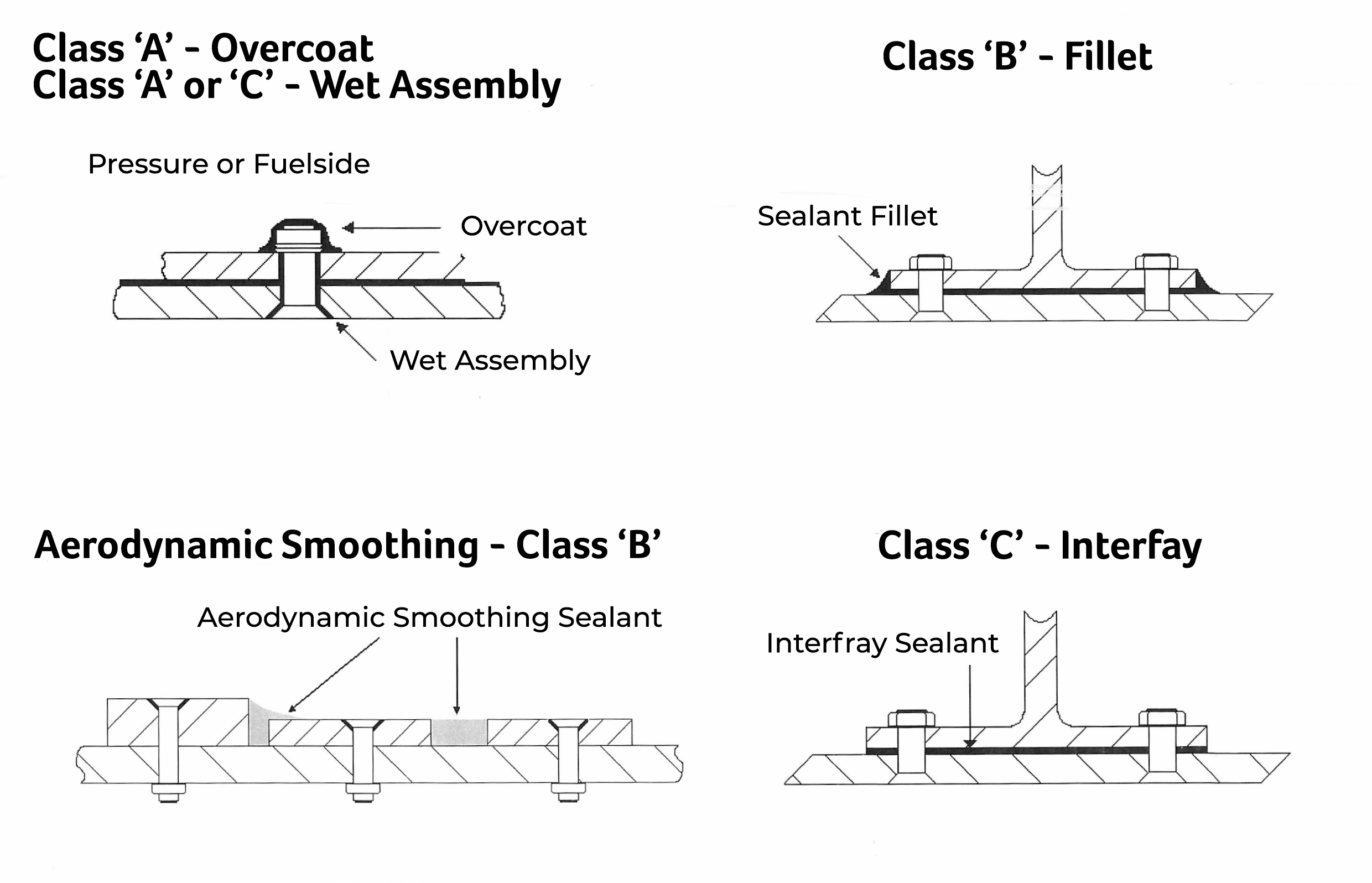
Aircraft Sealant Classes and Types
Sealants can generally be classified into 3 classes – A, B and C – although an S class does apply in some cases where a sealant can be sprayed.
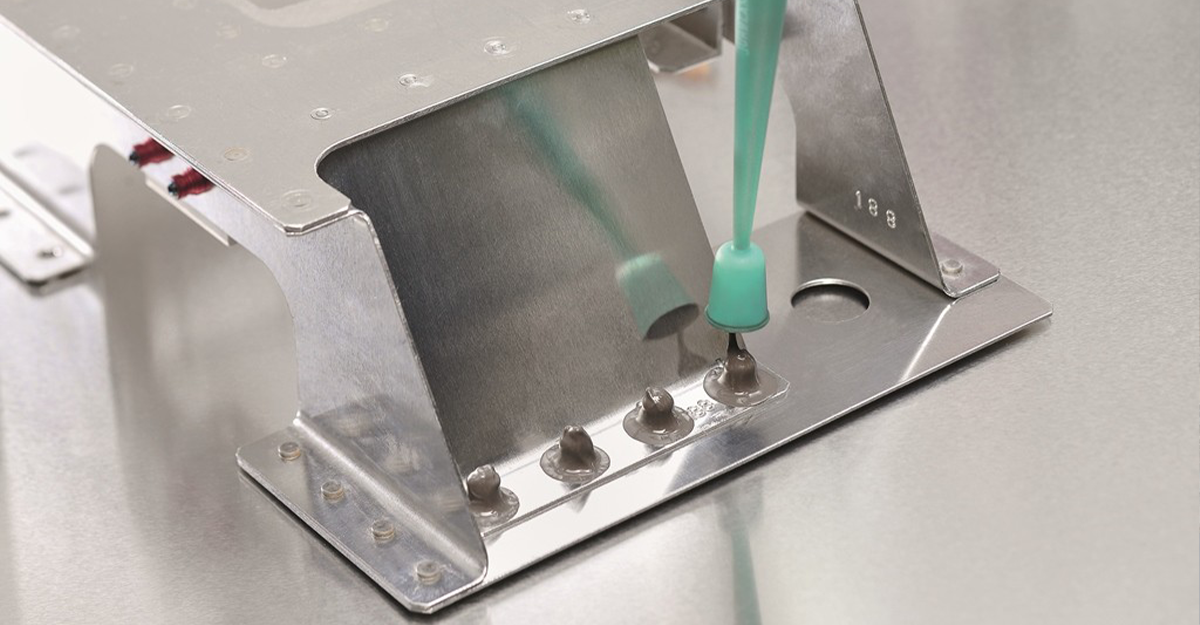
Class A – Brush application, generally used on fasteners
Class B – Thicker consistency, used for fillet and injection seals
Class C – Thinner than Class B, used for fay sealing
Aircraft Sealant Application Time Considerations
Different aircraft sealant application times are important as the nature of the work being carried out will vary depending on application. Where there is a large surface to be covered, a longer application time is necessary to ensure that the first product applied does not cure before the application work has been completed. Shorter application times are essential for time critical work, where the seal needs to be almost immediate.
How do I remove aircraft sealant?
In MRO applications, cured aircraft sealant may need to be removed to allow access to all areas of the aircraft. Similarly, during manufacture, assembly and resealing applications, uncured or semi-cured sealants may need to be cleaned prior to releasing the part.
There are a number of accessories suited to the specific removal of aircraft sealant from Socomore and PPG Semco.